Step by Step 커널 프로그래밍 강좌⑤
작성자 정보
- 웹관리자 작성
- 작성일
컨텐츠 정보
- 12,544 조회
- 0 추천
- 목록
본문
Step by Step 커널 프로그래밍 강좌⑤
파일시스템마운트
이번 강좌에서는 파일 시스템의 동작과정에 대하여 알아보기로 한다. 파일 시스템의 read/write에 대한 내용은 다른 많은 리눅스 커널 책에도 잘 소개되어 있다. 그러므로 이번 강좌와 다음 강좌에서는 파일 시스템의 마운트 과정에 대하여 자세히 분석하며 파일 시스템의 동작 과정을 이해하도록 할 예정이다.
글 _ 김민찬 KLDP 멤버, 전문 프로그래머
연재 순서
① 커널 프로그래밍 환경 구축하기와 특징
② 모듈 구현하기
③ 리눅스 커널의 메모리 관리
④ 커널의 동기화에 관하여
⑤ 파일 시스템 마운트 1
⑥ 파일 시스템 마운트 2
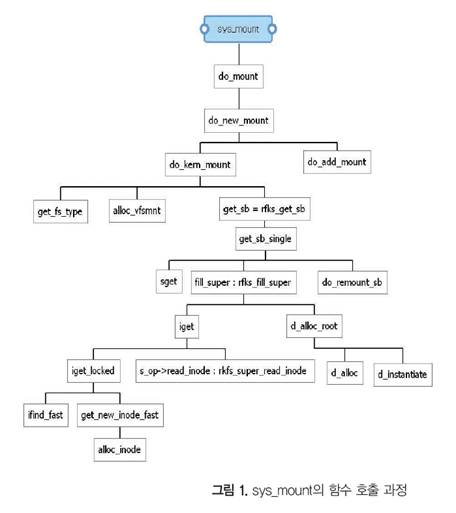
sys_mount의 함수 호출 과정을 항상 참조하라
이번 강좌에서는 파일 시스템의 분석을 위해 간단한 파일 시스템을 사용하며 분석할 것이다. rkfs라는 파일 시스템이며 이 파일 시스템에 관련된 사항은 다음 URL을 참조하면 된다.
http://www.geocities.com/ravikiran_uvs/articles/rkfs.html
먼저 사용자가 파일시스템을 mount를 하게 되면 커널의 다른 system call들과 마찬가지로 커널의 sys_mount 함수가 호출된다.
먼저 sys_mount를 분석하기 전에 주의 사항이 있다. 이 함수는 여러 중요한 함수들이 굉장히 깊이 있게 연결되어 있다. 그러므로 소스를 분석하다 보면 자신이 지금 어디에 서있는지 길을 잃어버리는 경우가 많다. 그러므로 항상 [그림 1]을 참조하여 자신이 지금 어느 곳에 서있는지 기억하고 있어야 할 것이다.
sys_mount는 인자로 넘겨받은 데이터들을 커널 메모리에 복사한 후, 실제적인 mount operation을 처리하는 do_mount 함수를 호출한다.
do_mount 함수는 기본적인 sys_mount 함수의 C++ overriding과 같은 역할을 한다. 즉 넘겨받은 파라미터 flags에 따라서 실제 일을 담당하는 함수 중 하나를 호출해준다. 호출되는 함수들은 다음과 같다.
● do_remount : flags에 MS_REMOUNT 옵션이 있을 때
● do_loopback : flags에 MS_BIND 옵션이 있을 때
● do_move_mount : flags에 MS_MOVE가 있을 때
● do_new_mount: 그 외의 모든 경우
위의 함수를 호출하기 전, 먼저 sys_mount로부터 넘겨받은 파라미터들의 간단한 유효성 검사를 수행한다. 그 다음 mount point의 dentry, vfsmount 등의 구조체를 얻어오기위하여 path_lookup 함수를 호출한다. vfsmount는 다음과 같은 필드를 갖는다.
struct vfsmount
{
struct list_head mnt_hash;
struct vfsmount *mnt_parent; // 우리의 vfsmount가 마운트된 파일이 속해있는 vfsmount
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; /* mount point 파일 과 관련된 dentry /*
struct dentry *mnt_root; /* root of the mounted tree */
struct super_block *mnt_sb; /* vfsmount의 root inode와 관련된 superblock */
struct list_head mnt_mounts; /* 이 vfsmount에 children vfsmount들의 리스트 /*
struct list_head mnt_child; /* child간의 연결 리스트 /*
atomic_t mnt_count;
int mnt_flags;
int mnt_expiry_mark; /* true if marked for expiry */
char *mnt_devname; /* Name of device e.g./dev/dsk/hda1 */
struct list_head mnt_list;
struct list_head mnt_fslink; /* link in fs-specific expiry list */
struct namespace *mnt_namespace; /* containing namespace */
};
표 1. vfsmount 구조체
do_new_mount 함수에 대한 호출
다음으로 do_new_mount 함수에 대한 호출을 살펴볼 것이다.
do_new_mount는 다음과 같이 호출된다.
static int do_new_mount(struct nameidata *nd, char *type, int flags,
int mnt_flags, char *name, void *data)
{
struct vfsmount *mnt;
if (!type || !memchr(type, 0, PAGE_SIZE))
return -EINVAL;
/* we need capabilities... */
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
mnt = do_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
return PTR_ERR(mnt);
return do_add_mount(mnt, nd, mnt_flags, NULL);
}
코드 1. do_new_mount
이 함수는 파라미터로 nameidata 구조체와 type, flags,mnt_flags, mount되는 device name, data_page를 받는다. 함수는 이 함수는 do_kern_mount 함수를 호출하여 superblock, dentry, address_space와 관련된 구조체들을 생성하고 연결한다. 그런 후 do_add_mount 함수를 호출하여
namespace tree에 연결시킨다. 각 함수를 자세히 살펴보기로 하자.
do_kern_mount() 함수는 다음과 같다.
struct vfsmount *
do_kern_mount(const char *fstype, int flags, const
char *name, void *data)
{
struct file_system_type *type = get_fs_type(fstype);
struct super_block *sb = ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int error;
char *secdata = NULL;
if (!type)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
if (!mnt)
goto out;
...
sb = type → get_sb(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(sb))
goto out_free_secdata;
error = security_sb_kern_mount(sb, secdata);
if (error)
goto out_sb;
mnt → mnt_sb = sb;
mnt → mnt_root = dget(sb → s_root);
mnt → mnt_mountpoint = sb → s_root;
mnt → mnt_parent = mnt;
mnt → mnt_namespace = current → namespace;
up_write(&sb → s_umount);
put_filesystem(type);
return mnt;
코드 2. do_kern_mount
이 함수는 먼저 get_fs_type에 아규먼트로 패스된 fstype을 패스 하 여 mount 하 려 는 파 일 시 스 템 의 구 조 체 인 file_system_type 구조체를 찾는다
struct file_system_type {
const char *name;
int fs_flags;
struct super_block *(*get_sb)
(struct file_system_type *, int,
const char *, void *);
void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *);
struct module *owner;
struct file_system_type * next;
struct list_head fs_supers;
};
코드 3. file_system_type 구조체
이 구조체는 register_filesystem 함수로 파일시스템을 등록할 때 파라미터로 사용된다. 위 구조체의 필드 중 가장 중요한 필드는 get_sb 함수 포인터이다. 이 함수는 파일시스템 개발
자가 커널에 있는 VFS(Virtual Filesystem Layer)에 hook(갈고리)를 걸어 놓는 것이다. 이렇게 callback 함수를 두는 이유는 VFS에 general한 인터페이스를 이용하되 자신에 입맛에 맞게 부분을 수정하려는 것이다. 위의 함수 get_sb는 superblock에 대한 초기화를 담당하게 되는데 각 파일시스템별로 superblock의 많은 필드들이 서로 다르다. 그러므로 커널은 위와 같은 hook을 걸 수 있는 인터페이스를 제공하여 파일시스템 개발자들에게 꿈과 희망을 주는 것이다.
그 다음으로는 alloc_vfsmnt를 호출하여 아규먼트로 넘어온 name에 해당하는 vfsmount 구조체를 만든다. 이때 vfsmount는 mnt_cache를 통하여 만들어지며 여러 필드들이 초기화된다. 아규먼트로 패스된 name은 vfsmount 구조체필드의 mnt_devname에 저장된다.
파일 시스템의 Specific Layer로 넘어가자
다음은 get_sb를 호출한다. 이 부분에서 우리는 최초로 VFS의 generic한 layer에서 파일 시스템의 Specific한 Layer로 넘어온 것이다. 필자는 filesystem의 specific한 부분에 대한 이해를 돕기 위하여 간단한 ram file system인 rfks를 예를 들어 설명한다. (rfks 소스 - 부록 참고). get_sb 함수는 rfks의 file_system_type은 다음과 같이 정의되어 있다
static struct file_system_type rkfs = {
name: "rkfs",
get_sb: rkfs_get_sb,
관련자료
-
이전
-
다음




